What Are IEC 60502 Cables and Why Are They Essential?
IEC 60502 cables are power cables with extruded solid insulation that meet international construction, dimension and testing standards established by the International Electrotechnical Commission. The standard divides into 2 main parts covering different voltage applications. IEC 60502-1 specifies cables for rated voltages of 0.6/1kV and 1.8/3kV used in low voltage applications. IEC 60502-2 covers cables from 3.6/6kV up to 18/30kV for medium voltage distribution systems.
These cables form the backbone of modern electrical infrastructure. Power utilities, industrial facilities and commercial installations rely on IEC 60502 cables to deliver consistent electrical supply. The standard ensures cables withstand electrical stresses, mechanical forces and environmental conditions encountered during installation and service.
Which Industries and Applications Require IEC 60502 Cables?
Key Sectors
IEC 60502 cables serve fixed installations across 5 primary sectors: oil and gas facilities, power generation and renewable energy plants, utilities including DNOs and IDNOs, rail infrastructure, and EV charging networks.
Specific Applications
Power stations require robust cabling that operates reliably under demanding conditions. Distribution networks depend on IEC 60502 cables to transmit electricity from substations to end users. Industrial installations in petrochemical plants demand cables that resist hydrocarbons and chemical exposure.
Installation Environments
Mass transit systems use these cables in underground passenger networks where fire performance characteristics protect public safety. EV charging infrastructure relies on cables that handle high current loads whilst maintaining safety standards.
The cables suit indoor applications, outdoor installations, underground burial and submersion in water. Installation methods include direct burial in free-draining soil, placement in cable ducts, clipping to surfaces, and mounting on cable trays. Each application benefits from the standard’s comprehensive specification of conductor materials, insulation types and protective layers.
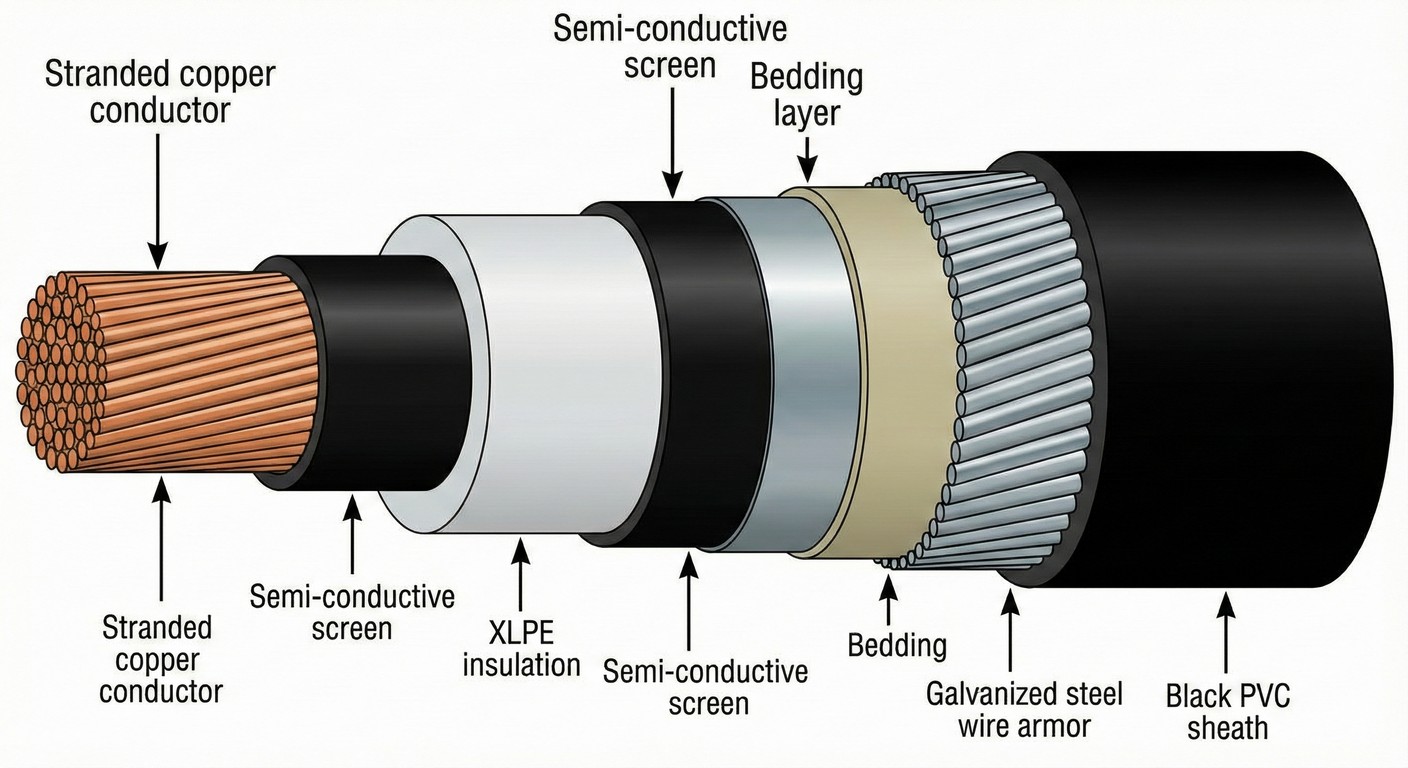
What Construction Standards Define IEC 60502 Cables?
IEC 60502 cables feature 5 essential construction elements: conductors complying with authoritative international standards, extruded insulation layers, screening systems, protective sheaths, and optional armour for mechanical protection.
Conductors
Conductors comprise Class 1 solid or Class 2 stranded configurations. Materials include plain annealed copper, metal-coated copper, plain aluminium or aluminium alloy. Copper conductors offer superior conductivity whilst aluminium provides weight and cost advantages. Conductor cross-sections range from 1.5mm² to 1600mm² depending on current requirements.
Insulation Materials
Insulation types include 4 primary materials. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) serves cables rated up to 3.6/6kV with operating temperatures to 70°C. Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) provides superior thermal performance with 90°C continuous operation and 250°C short-circuit capability. Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) and high modulus EPR (HEPR) offer flexibility and electrical properties for demanding applications.
Screening Layers
Screening layers surround insulated cores in medium voltage cables. Conductor screens consist of extruded semi-conducting compounds bonded to insulation. Insulation screens combine non-metallic semi-conducting layers with metallic components. Metallic screens use copper tape or concentric copper wires to provide earth fault current paths.
How Do Voltage Ratings and System Categories Work?
IEC 60502 cables carry voltage designations expressed as U0/U(Um) where U0 represents the rated voltage between conductor and earth, U indicates voltage between conductors, and Um denotes maximum system voltage.
Low voltage cables include 0.6/1(1.2)kV and 1.8/3(3.6)kV ratings. Medium voltage specifications span 3.6/6(7.2)kV, 6/10(12)kV, 8.7/15(17.5)kV, 12/20(24)kV and 18/30(36)kV. Each rating suits specific distribution system requirements.
The standard defines 3 system categories based on earthing practices. Category A systems disconnect earth faults within 1 minute. Category B systems operate with one phase earthed for periods not exceeding 8 hours per occasion and 125 hours annually. Category C encompasses all systems outside Categories A and B. System category determines appropriate cable selection and insulation thickness requirements.
What Insulation Thickness Requirements Apply?
Insulation thickness varies according to 3 factors: rated voltage, conductor cross-sectional area, and insulation material type.
-
IEC 60502-1 specifies minimum insulation for low voltage applications. Cables rated 0.6/1kV require 0.7mm insulation for XLPE and EPR materials on conductors from 1.5mm² to 300mm². Cables rated 1.8/3kV use thicker insulation calculated as 0.7mm plus 0.015 times the conductor diameter.
-
IEC 60502-2 establishes greater insulation thickness for medium voltage. Cables rated 3.6/6kV require 3.4mm insulation on conductors from 10mm² to 1600mm². Higher voltage ratings increase insulation thickness progressively. Cables rated 18/30kV use 8.0mm insulation to withstand electrical stresses.
-
Insulation thickness protects against electrical breakdown during normal operation and testing. Thicker insulation reduces maximum electrical stress applied to materials. Standards permit increased thickness on large conductors above 1000mm² to prevent mechanical damage during installation.
🧮 Free Cable Size Calculator
You determine correct cable sizes. You input voltage parameters. You input load requirements. Our tool ensures BS 7671 compliance. You avoid costly specification errors.
Which Armour Options Provide Mechanical Protection?
IEC 60502 armoured cables feature 2 primary protection types: steel wire armour (SWA) for multicore cables and aluminium wire armour (AWA) for single core cables.
Steel Wire Armour (SWA)
Steel wire armour consists of galvanised steel wires applied helically over cable cores. SWA provides excellent protection against mechanical impact, crushing forces and damage during installation. The galvanised coating resists corrosion in buried applications. Steel armour suits three-core cables and applications where magnetic properties do not affect performance.
Aluminium Wire Armour (AWA)
Aluminium wire armour uses non-magnetic aluminium wires for single-core cables in AC systems. AWA prevents induced currents that occur when ferromagnetic materials surround single conductors carrying alternating current. The lighter weight simplifies handling and installation compared to steel alternatives.
Additional Armour Types
Steel tape armour offers an alternative for certain applications. Double steel tape layers provide longitudinal strength and radial protection. Non-magnetic stainless steel tape suits single-core AC cables whilst galvanised steel tape serves multicore constructions.
Armoured cables include separation sheaths between cores and armour. Bedding layers comprise extruded PVC, polyethylene or LSZH compounds with thickness calculated from core assembly diameter. Outer sheaths applied over armour protect metallic layers from corrosion whilst contributing to fire performance.
What Are Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) Cable Benefits?
LSZH cables manufactured to IEC 60502 exhibit 3 critical fire safety characteristics: reduced flame spread, low smoke emission under 40% obscuration, and zero halogen content producing less than 0.5% hydrogen chloride gas.
Standard PVC cables release dense black smoke containing up to 30% hydrogen chloride when burning. Smoke obscures escape routes whilst toxic fumes incapacitate occupants. Hydrogen chloride combines with moisture to form hydrochloric acid that damages electronic equipment and corrodes building infrastructure.
LSZH compounds eliminate halogens from cable construction. Materials produce minimal smoke with light transmittance exceeding 60% in standard tests. Toxic gas emissions remain below harmful thresholds. These properties prove essential in public buildings, underground transit systems, hospitals, airports and data centres where evacuation and equipment protection require clear visibility.
We supply LSZH variants across our IEC 60502 cable range. Constructions replace PVC bedding and sheaths with halogen-free thermoplastic compounds designated ST8. LSZH insulation maintains electrical properties whilst meeting fire performance standards established by authoritative testing organisations.
How Do Water Blocking Features Protect Cable Integrity?
Water blocking technology prevents moisture ingress through 2 mechanisms: swellable tapes that expand when wetted and powder compounds that absorb water within cable voids.
Water penetration causes premature cable failure in buried and submerged applications. Moisture compromises insulation resistance leading to tracking and breakdown. Water migration along conductor strands extends damage beyond the initial ingress point. Research from authoritative sources indicates medium voltage cable accessories account for 80% of system failures, primarily from improper sealing and moisture entry.
Longitudinal water blocking uses swellable materials applied over insulation screens or within conductor interstices. Tapes contain polymers that swell when contacted by water, forming barriers that prevent axial water movement. Class 2 stranded conductors may incorporate water blocking if installation conditions demand protection.
The IEC 60502 standard includes specifications for water blocking performance. Cables designed for wet locations, flood-prone areas or direct burial benefit from these protective features. We provide water blocked variants across medium voltage ranges serving utilities and infrastructure projects in demanding environments.
What Testing Requirements Ensure Cable Quality?
IEC 60502 mandates 3 test categories: routine tests performed on every cable length, sample tests conducted at specified frequencies, and type tests demonstrating design compliance before commercial supply.
Electrical Tests
Electrical type tests verify insulation integrity and performance. Partial discharge tests detect manufacturing defects by measuring discharge levels at 1.73 times rated voltage. Voltage withstand tests apply 4 times rated voltage for 4 hours at ambient temperature. Impulse tests subject cables to lightning surge voltages simulating switching transients. Heating cycle tests combine electrical stress with thermal loading at conductor temperatures reaching 98°C.
Non-Electrical Tests
Non-electrical tests evaluate mechanical and thermal properties. Insulation thickness measurements confirm compliance with dimensional specifications. Tensile strength and elongation tests assess material properties before and after accelerated ageing. Hot set tests for XLPE verify crosslinking quality. Shrinkage tests ensure dimensional stability during service.
Component & System Tests
Tests on cable components examine conductor resistance, screening resistivity and sheath properties. PVC sheaths undergo heat shock tests demonstrating crack resistance. All materials face ageing protocols that simulate long-term exposure to elevated temperatures.
Electrical tests after installation verify system integrity. Authoritative testing procedures establish voltage levels and test duration based on cable construction. Tests identify damage from installation whilst confirming proper accessory connection.
How Do We Support Your IEC 60502 Cable Requirements?
We deliver 4 comprehensive services: nationwide stock availability across 5 branches, cutting and kitting operations for project-specific requirements, product familiarisation training in Wrexham and Glasgow facilities, and technical expertise supporting cable selection and specification.
-
Our branches maintain inventory of IEC 60502 cables in common voltage ratings and conductor sizes. Single-core and multicore constructions suit diverse applications. Copper and aluminium conductor options provide flexibility for project budgets and performance requirements. PVC and LSZH sheathed variants meet different fire performance specifications.
-
Project support includes cable cutting to precise lengths and custom kitting for installation sequences. Technical staff assist with current rating calculations, installation method selection and compliance verification. Training programmes familiarise installation teams with cable handling, jointing procedures and testing protocols.
-
We source cables from market-leading manufacturers ensuring consistent quality and full compliance documentation. Approvals from recognised certification bodies verify conformance to IEC 60502 requirements. Traceability systems track cable batches from manufacturing through delivery.
Why Choose Cable Services for IEC 60502 Cable Supply?
Cable Services combines 5 decades of industry experience with comprehensive product knowledge, rapid response capabilities, nationwide distribution infrastructure, and commitment to customer-focused service.
Since our founding in 1971, we built lasting relationships with organisations throughout the energy sector. Our expertise spans utilities, power generation, oil and gas, rail and emerging EV infrastructure markets. Deep understanding of sector-specific requirements informs cable recommendations and technical support.
State-of-the-art training facilities demonstrate cable installation techniques and accessory application. Hands-on programmes cover low voltage through 132kV systems. Customers gain practical skills reducing installation time and ensuring reliable connections.
Our responsive service model prioritises customer requirements. Flexible delivery schedules support project timelines. Emergency supply capabilities maintain operations during unplanned outages. Dedicated account management provides consistent contact and project continuity.
We maintain strong supplier relationships ensuring access to specialist cables and emerging technologies. Partnership with leading manufacturers provides early access to product innovations meeting evolving standards and application demands.
Request A Custom Quotation